Search results for 'Paul Gauguin' at the museum of art
Exhibitions
Paul Gauguin
Artists: Paul Gauguin
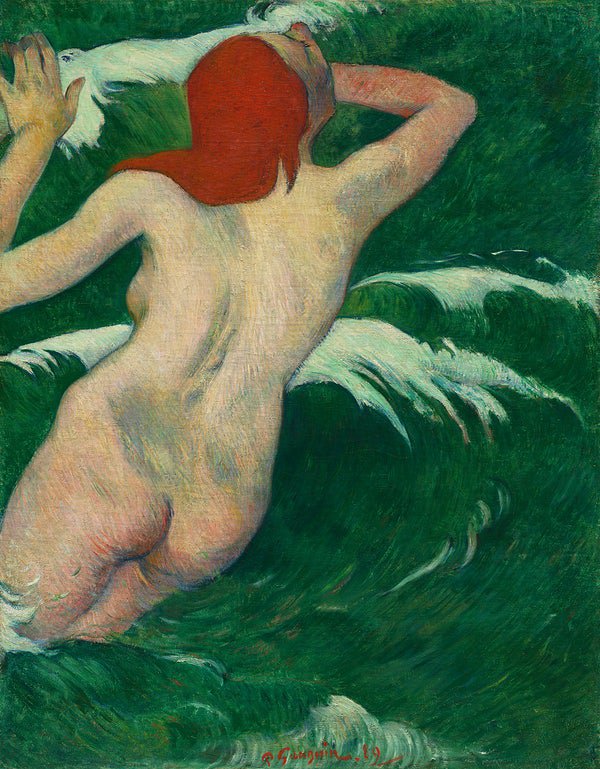
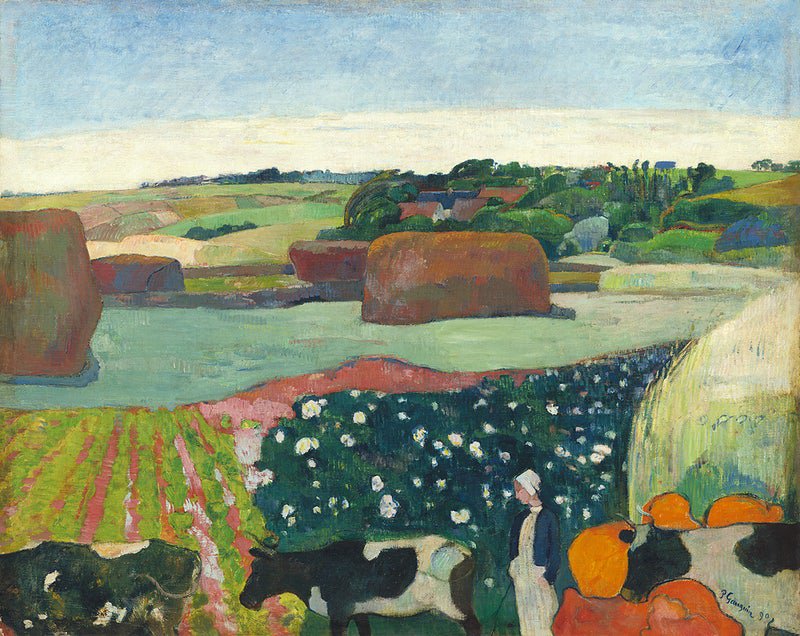
Paul Gauguin or Eugène Henri Paul Gauguin (7 June 1848 – 8 May 1903) was one of the most influential Post-Impressionist artists. Gauguin's experimental use of color and stark contrasts spearheaded the Synthetism movement, which regarded form and color as equally important. Most of his paintings depict people or landscapes from French Polynesia since he spent many years in that region in search of inspiration. His artistic experiments influenced many avant-garde movements in the early 20th century as well as modern artists such as Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse.
Henri Paul Gauguin was a French Post-Impressionist artist and unappreciated until after his death, Gauguin is now recognized for his experimental use of color and Synthetist style that were distinct from Impressionism. Toward the end of his life, he spent ten years in French Polynesia. The paintings from this time depict people or landscapes from that region.
His work was influential to the French avant-garde and many modern artists, such as Pablo Picasso and Henri Matisse. Gauguin's art became popular after his death, partially from the efforts of art dealer Ambroise Vollard, who organized exhibitions of his work late in his career and assisted in organizing two important posthumous exhibitions in Paris.
Gauguin was an important figure in the Symbolist movement as a painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramist, and writer. His expression of the inherent meaning of the subjects in his paintings, under the influence of the cloisonnist style, paved the way to Primitivism and the return to the pastoral. He was also an influential proponent of wood engraving and woodcuts as art forms.